Overview
The General Storage Cluster Controller is a high-availability solution specifically designed for the IBM Spectrum Protect servers. GSCC is not a mere server cluster, but an application cluster that is tailored to the requirements of ISP servers. As this solution is focused on the application not only hardware failures, but also functional errors and logical problems of the application can be monitored and resolved if necessary.
GSCC manage single ISP server instances as independent objects. Each of these instances can be prevented from fulfilling their actual tasks due to a number of different errors. GSCC analyzes these errors and fixes them deliberately and with reasonable means. In contrast to traditional clustering solutions the application is not simply shifted to another system, if the error can be solved locally or the shift would not solve the problem. GSCC monitors all ISP instances and continuously checks their functionality and associated resources and components (DB2, storage pools, LAN connection, etc.).
If the error states cannot be solved locally, GSCC initiates the takeover by another system. If the error persists there as well, possibly more drastic corrections are required. GSCC can even respond to errors in the ISP database and fall back to a consistent standby copy of the database if necessary.
These additional steps and functions can also be performed manually and accurately with GSCC. TSM server instances can be started, stopped and moved via a GUI or Command Line in order to perform configuration changes, hardware or software maintenance to even for load balance reasons. Storage agent and TSM client environments are transparently serviced by the cluster.
GSCC is a very flexible and configurable cluster solution. It supports several takeover scenarios by utilizing two main takeover mechanisms, which can be combined or differently prioritized:
- Shared disk failover
Volume Manager Failover like LVM
Shared Filesystem like GPFS
- Standby database failover
DB2 HADR (High Availability Disaster Recovery) log shipping
The shared disk failover describes the switch of a productive database from one UNIX system to another by accessing the original disk volumes containing ISP configuration, database and logs. These volumes could be SAN disks configured with AIX LVM, Veritas VM, SVM, ZFS or GPFS. The standby failover refers to the activation of a second independent database copy not sharing any database resources with the productive ISP instance. This is based on the DB2 function HADR (High Availability Disaster Recovery). HADR allows the synchronizing level to be defined from asynchronous up to fully synchronous.
Based on a HADR synchronous (nearsync) standby copy GSCC supports HADR only clusters with no shared database disk resources (IP cluster).
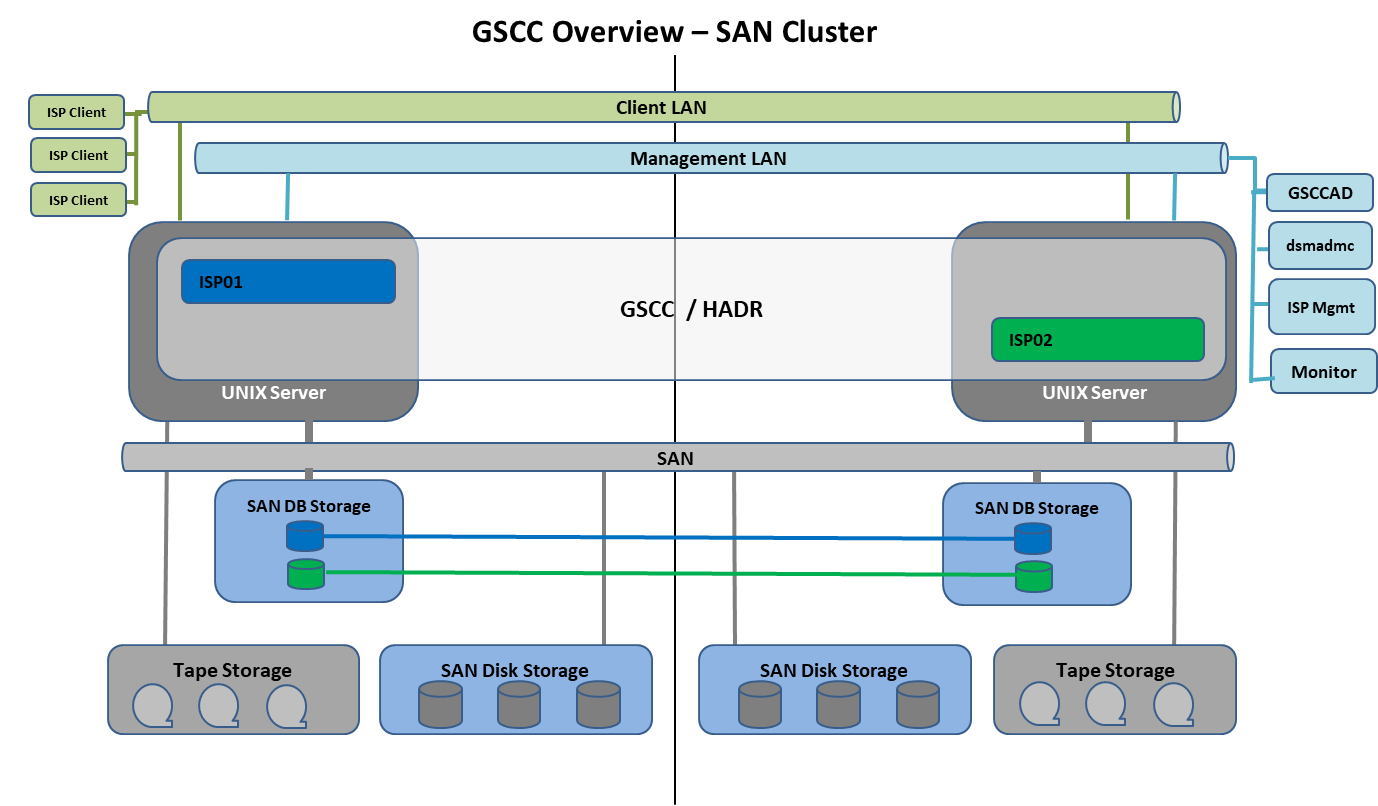
GSCC Overview – SAN Cluster
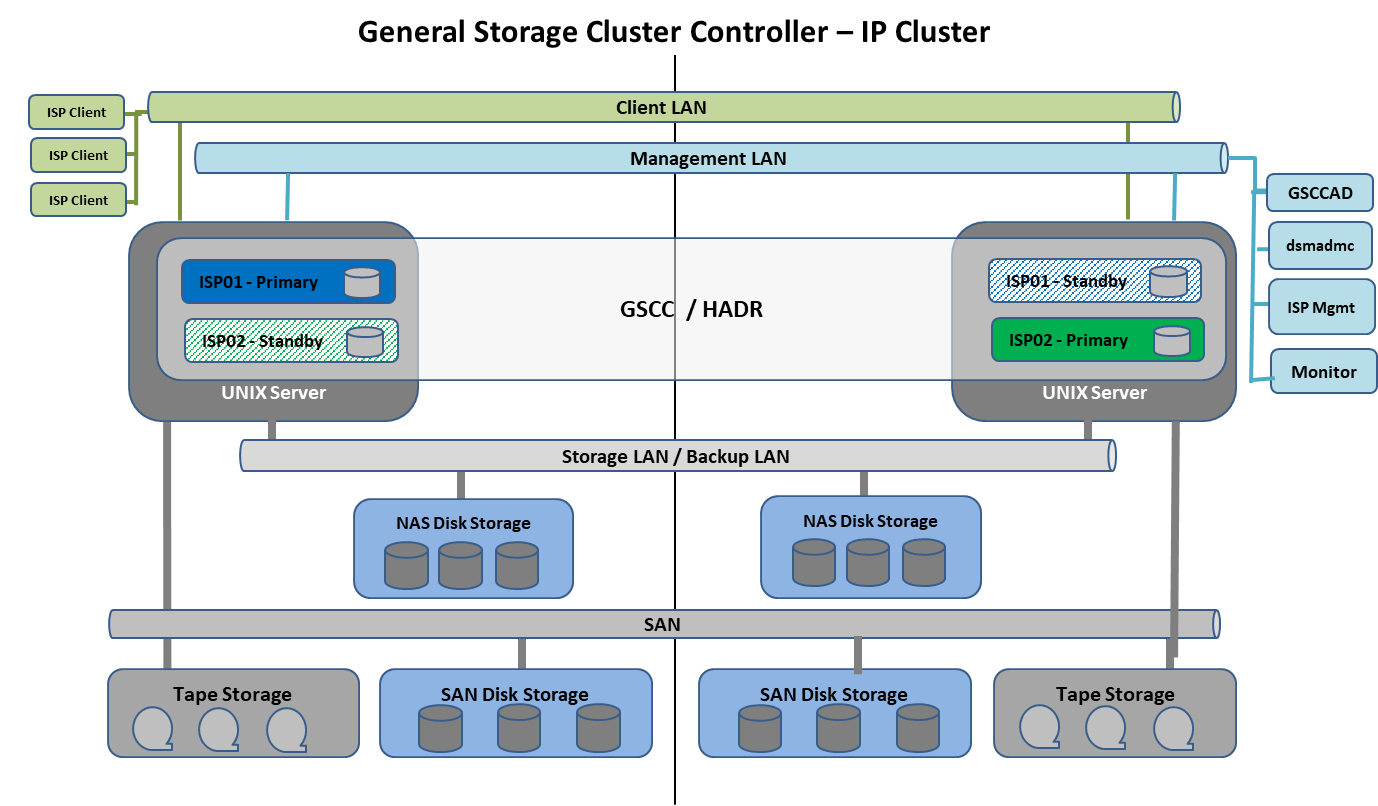
GSCC Overview – IP Cluster
There are certain advantages and disadvantages to the different failover methods and the decision depends on the requirements. However, the way GSCC reacts can be easily changed by using just different “rulesets” defined in a so-called expert domain.
GSCC takes care about the ISP resources including the volume management tasks in a shared disk scenario and the HADR tasks in a standby failover situation. Most important GSCC also takes care about the TSM server process itself and the IP addresses used by TSM clients and storage agents.